South African Plastics Industry
The South African plastics market is well developed throughout the plastics value chain and caters to both local demand and export markets. Generally, the leading markets for plastics are in packaging, building, construction and the automotive industries. However, a number of other industries which use some form of plastic are textile, electrical, electronic, mechanical engineering, and agricultural industries.
These industries have struggled to adjust to changes in the market due to a downturn in demand, rising tide of imports and competition from advanced developing countries. More so, cheap imports of relatively low added-value products are causing some parts of the world’s plastics industry to restructure.
The contribution to the GDP in 2018 was calculated at more than 2.1 % and 21.8 % contribution to the Manufacturing GDP. There are approximately 1 800 companies employing around 60 000 workers in the sector.
Market sectors
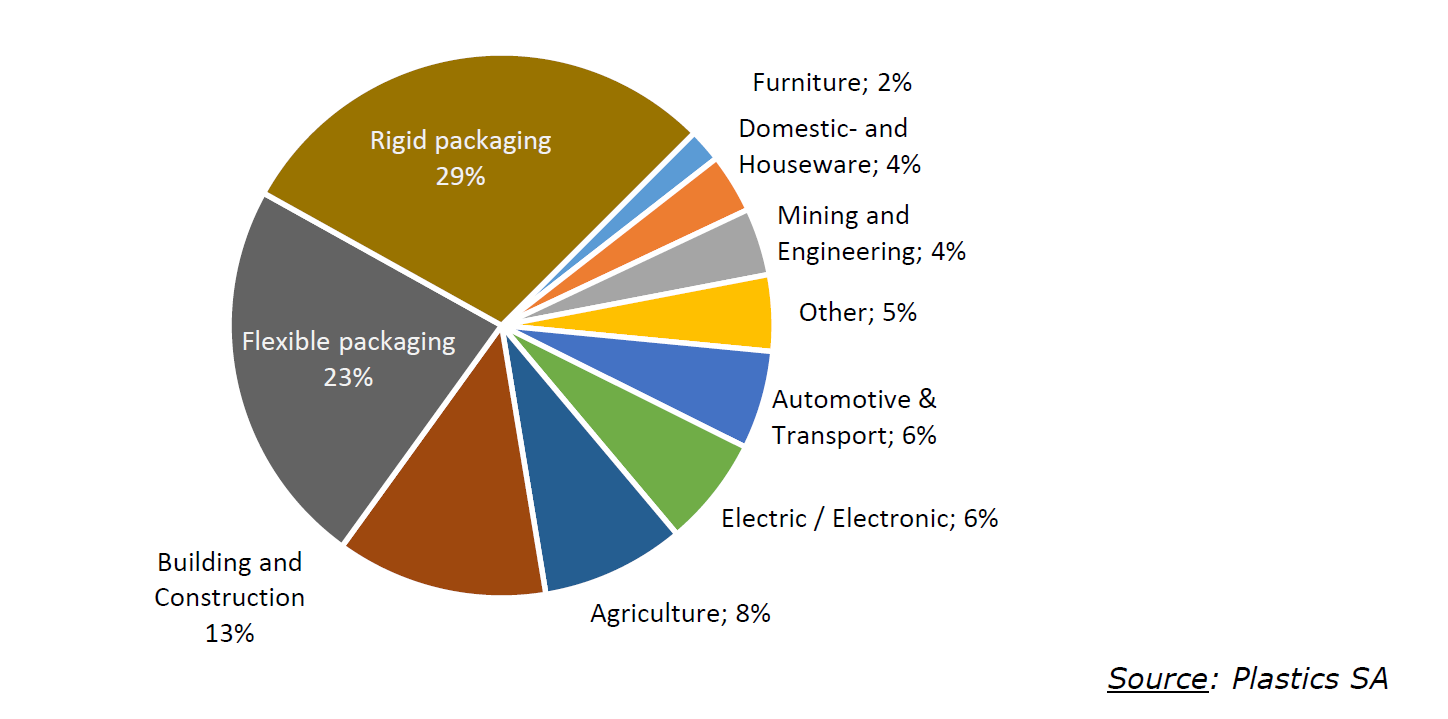
Plastics form an integral part of our lives and is found in just about every aspect. South Africa’s plastics industry is dominated by the packaging industry which accounts for 52 % of the local market followed by Building and Construction at 13 % and Agriculture at 8 %.
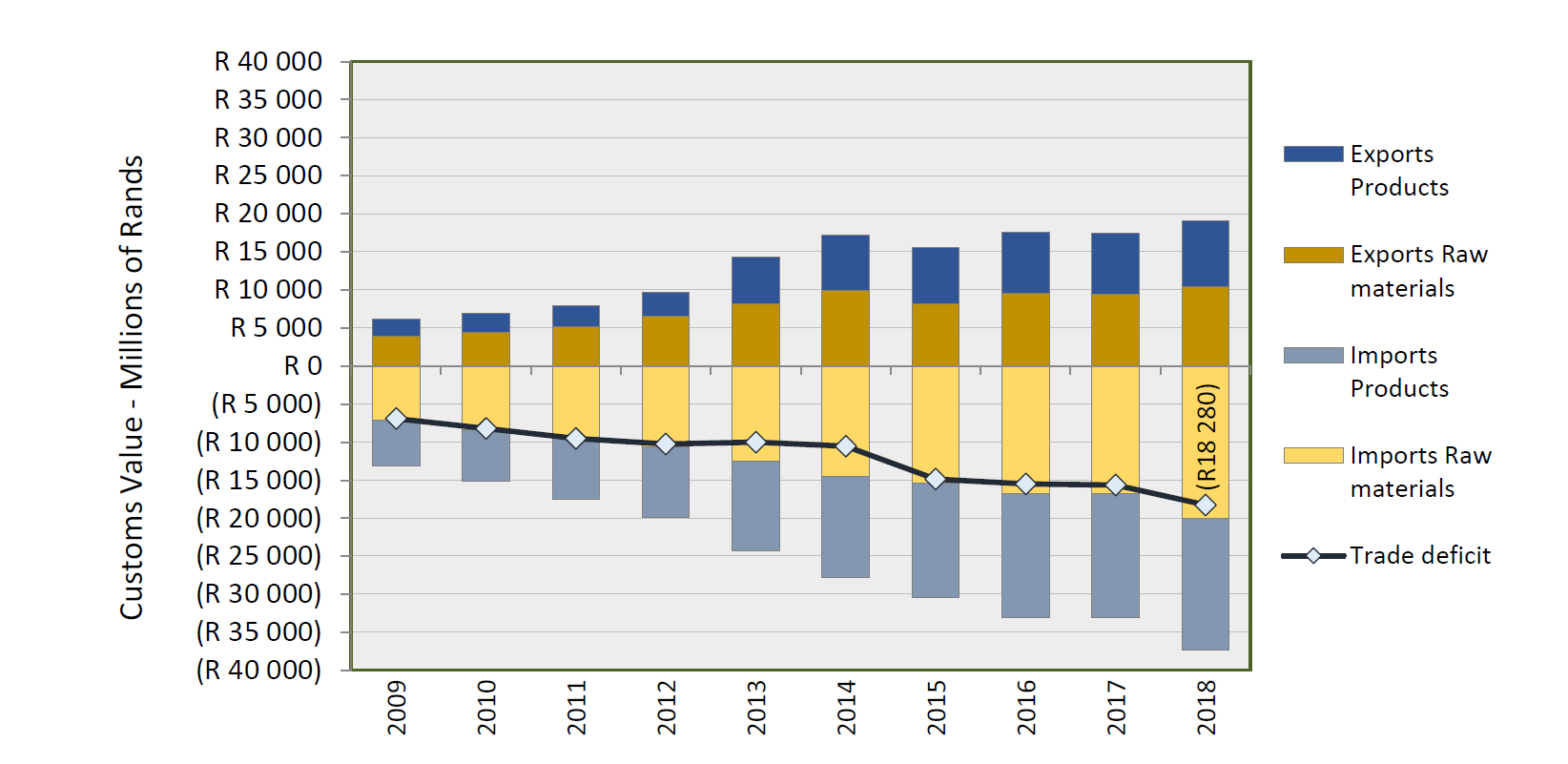
Trade balance
A large volume of the total domestic consumption is produced from locally produced ethylene. The manufactured tonnages of PE-LD, PE-LLD and PE-HD is not meeting all of the local requirements. The manufacturing capacity of PP exceeds local demand and because of this, a substantial amount of PP is exported. However, South Africa imports polyolefin polymers where specific grades are not locally produced, where seasonal shortages are experienced and, to have a second supplier account. Large quantities of finished and semi-finished plastics products are imported – also products made from the very same polymers that are exported.
Despite a large polymer producer in South Africa, the tonnages of polymer imported still exceed the exports, i.e. a trade deficit. In 2018, the total trade deficit was R18.3 billion whilst the total value of the domestic industry was estimated at R84.4 billion – a deficit of 21.6 %. The largest two contributors to the deficit in 2018 were PE-HD polymer imports (R1.9 billion) and “Other Articles Of Plastics And Articles: Other”, HS 39 26 90 90.
Constraints
Plastics conversion plants are generally small to medium-sized, with an average size of 130 employees. Many plants have fewer than 50 employees, and those with 400 or more employees are generally considered to be large. Constraints faced by the plastics sector include the following:
- Import parity pricing of polymers;
- Pricing of raw materials;
- Relative small local and regional market;
- Lack of advanced manufacturing practices;
- Lack of downstream focus on R&D effort; and
- South Africa’s geographic position and resultant logistics costs.
Key Opportunities
Key areas of opportunity for growing sector include the following:
- Automotive interior and exterior products;
- Food packaging;
- Medical products;
- Buildings- pipes, flooring and building sheet; and
- Electrical and electronics cables, appliances and casing components.

